Moving Beyond the Basics in MDM4U
Data Management
Chris Papalia
St. Andrew’s College
Original - 2017-05-17
(updated: 2021-03-16)
Resources Available here: http://bit.ly/BeyondBasicsMDM4U
Personal Website: http://highschoolteach-r.netlify.com/
Chris Papalia
Education Background
- B.A. Physics - Macalester College, 2007
- B.Ed. Mathematics and Physics - University of Toronto/OISE, 2009
- M.Ed. Curriculum, Teaching, Learning - University of Toronto/OISE, 2018
Chris Papalia
Education Background
- B.A. Physics - Macalester College, 2007
- B.Ed. Mathematics and Physics - University of Toronto/OISE, 2009
- M.Ed. Curriculum, Teaching, Learning - University of Toronto/OISE, 2018
Professional Background
- Durham District School Board 2009 – 2012
- St. Andrew’s College 2012 – Present
Chris Papalia
Education Background
- B.A. Physics - Macalester College, 2007
- B.Ed. Mathematics and Physics - University of Toronto/OISE, 2009
- M.Ed. Curriculum, Teaching, Learning - University of Toronto/OISE, 2018
Professional Background
- Durham District School Board 2009 – 2012
- St. Andrew’s College 2012 – Present
Interests
- Teaching Statistics
- Data Science and Analytics in R
- Tech Integration into Teaching
- Online Learning
- Coaching Hockey and Baseball and Squash
I am fortunate to have access to many resources, but in teaching in public schools for three years, I still believe that much of what I do now can be done in many schools.
St. Andrew's College
Outline
Outline
1. History
Outline
1. History
a. Know your audience
Outline
1. History
a. Know your audience
b. How I started teaching MDM4U
Outline
1. History
a. Know your audience
b. How I started teaching MDM4U
2. How I am changing
Outline
1. History
a. Know your audience
b. How I started teaching MDM4U
2. How I am changing
a. Order of Units
Outline
1. History
a. Know your audience
b. How I started teaching MDM4U
2. How I am changing
a. Order of Units
b. Context with Books/Media/Podcasts
Outline
1. History
a. Know your audience
b. How I started teaching MDM4U
2. How I am changing
a. Order of Units
b. Context with Books/Media/Podcasts
c. Spiral Topics
Outline
1. History
a. Know your audience
b. How I started teaching MDM4U
2. How I am changing
a. Order of Units
b. Context with Books/Media/Podcasts
c. Spiral Topics
d. Tech/Visualization/(coding?)
Outline
1. History
a. Know your audience
b. How I started teaching MDM4U
2. How I am changing
a. Order of Units
b. Context with Books/Media/Podcasts
c. Spiral Topics
d. Tech/Visualization/(coding?)
e. Assessing with projects
Who Takes Data Management?
Who Takes Data Management?
Students say...
Who Takes Data Management?
Students say...
- “I need a grade 12 math”
Who Takes Data Management?
Students say...
“I need a grade 12 math”
“Calculus and Advanced Functions are too hard”
Who Takes Data Management?
Students say...
“I need a grade 12 math”
“Calculus and Advanced Functions are too hard”
“I’m not a math person”
Who Takes Data Management?
Students say...
“I need a grade 12 math”
“Calculus and Advanced Functions are too hard”
“I’m not a math person”
“I don’t need math…”
Who Takes Data Management?
Students say...
“I need a grade 12 math”
“Calculus and Advanced Functions are too hard”
“I’m not a math person”
“I don’t need math…”
“Guidance said this is the math class for me”
Who Teaches Data Management?
Who Teaches Data Management?
Those who...
Who Teaches Data Management?
Those who...
...can't teach calculus?
My first time teaching MDM...
Teaching MDM is an opportunity...
My Journey
My Journey
When I started....
Student's were calculating the standard deviation by hand
Using a TI-83+ was considered tech
We rarely discussed data in the wild
My Journey
When I started....
Student's were calculating the standard deviation by hand
Using a TI-83+ was considered tech
We rarely discussed data in the wild
But now that I've taught this more...
We are using software to perform calculations and visualization
We spend most of our time interpreting statistical outputs
and telling stories with data visualization
The Data tells a story...
The Data tells a story
How did I change my practice?
Organized a New Course Plan
1. One Variable Data – “What’s the data say?”
- Distributions and Statistics (shape, centre, spread)
2. Normal Distributions and Standardized Scores - "How do we compare individuals"?
3. Two Variable Data – “What else is at play?”
4. Data Collection – “What say do we have in the data?”
5. Probability – “How likely is the data”
- Counting, permutations, combinations
6. Probability Applications and Distributions "How can I win with data?"
7. Special Topics in Data "How do I apply these skills"
Enrich the Classroom with Tools
Laptop, Projector, Live Data Analysis
Simulations, Excel, Fathom, RStudio
We try to work with data visualization every day
Remember, a good plot tells the story
Add context
Add context
Specific Improvements
Specific Improvements
1. Spiraling Content/Adding context
Always revisiting one/two variable data and looking ahead and behind
Specific Improvements
1. Spiraling Content/Adding context
Always revisiting one/two variable data and looking ahead and behind
2. Using tools that are accessible to students
Data Visualization with meaningful data
Low floor; High ceiling
Specific Improvements
1. Spiraling Content/Adding context
Always revisiting one/two variable data and looking ahead and behind
2. Using tools that are accessible to students
Data Visualization with meaningful data
Low floor; High ceiling
3. Using applets, discussion forums, and teaching videos
Recording class lessons
Student discussions
Specific Improvements
1. Spiraling Content/Adding context
Always revisiting one/two variable data and looking ahead and behind
2. Using tools that are accessible to students
Data Visualization with meaningful data
Low floor; High ceiling
3. Using applets, discussion forums, and teaching videos
Recording class lessons
Student discussions
4. Using AP Statistics Resources
Free-Response Questions that will connect several course topics
Model answers and rubrics available for students
Adding Context and Connecting Topics
Data, Probability, and Stories
Data, Probability, and Stories

Chapter 2: Probability
- Natural Variability
- Birthday and Monty Hall Problem
- Statistics and Probability
- Written with excellent prose and narrative
Data, Probability, and Stories

Chapter 2: Probability
- Natural Variability
- Birthday and Monty Hall Problem
- Statistics and Probability
- Written with excellent prose and narrative

The Creator of Gapminder
Data is available to reproduce these plots and Hans Rosling shares with us the stories these data tell
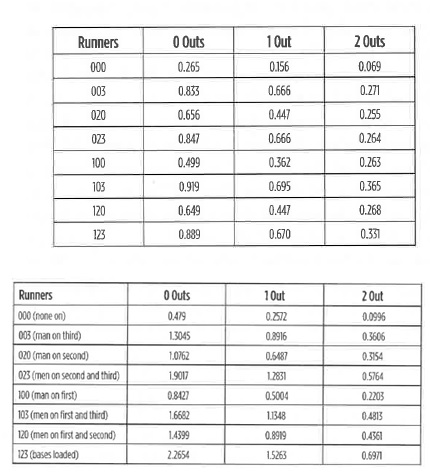
Expected Values, Probability, and Decisions
Expected Values, Probability, and Decisions
 The book describes decision making in baseball and outlines expected run probability and decision-making.
The book describes decision making in baseball and outlines expected run probability and decision-making.
Expected Values, Probability, and Decisions
 The book describes decision making in baseball and outlines expected run probability and decision-making.
The book describes decision making in baseball and outlines expected run probability and decision-making.
Podcasts For Context
Podcasts For Context
What Can Uber Teach us About the Gender Pay Gap?
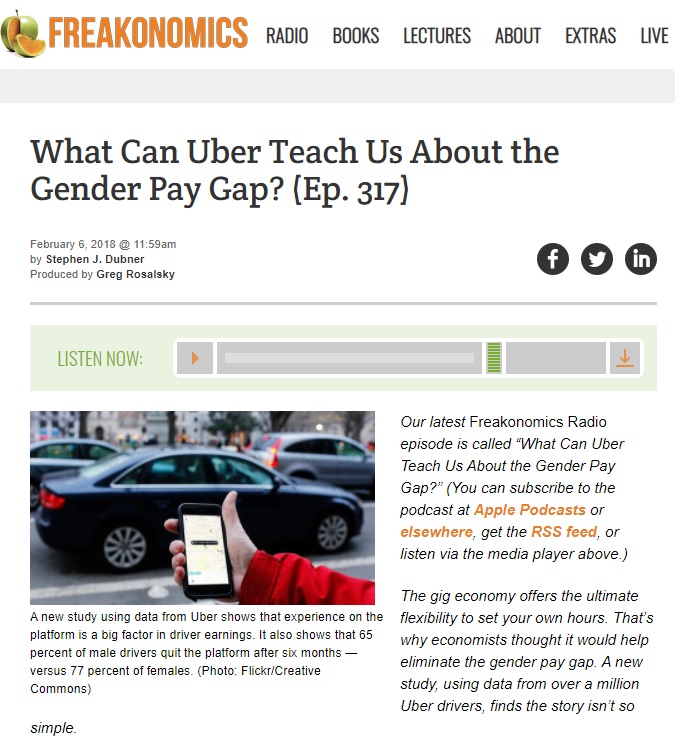
Study Design Principles
Exploring the Gender Pay Gap
"Explained Variance" and Modelling
Other podcasts exploring, research, statistics, economics, and social science:
Introduction to Two-Variable Data
The Most Diverse Cities are Often the Most Segregated (fivethirtyeight.com)
Introduction to Two-Variable Data
The Most Diverse Cities are Often the Most Segregated (fivethirtyeight.com)
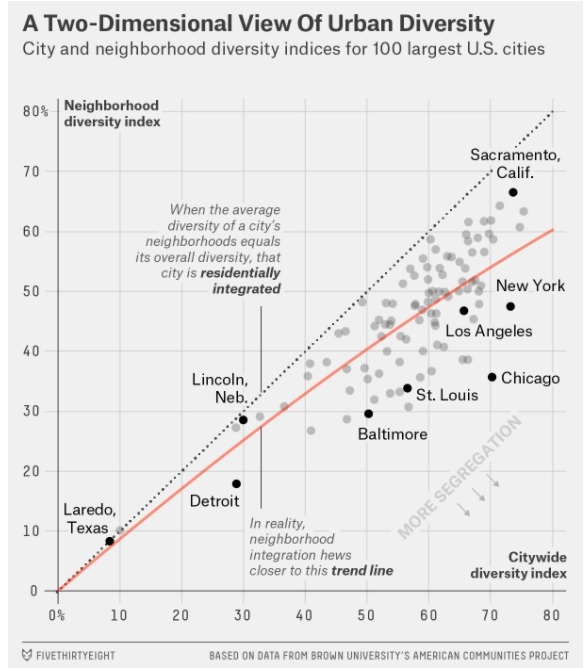
Introduction to Two-Variable Data
The Most Diverse Cities are Often the Most Segregated (fivethirtyeight.com)

Let's understand a scatterplot
Let's look at a regression model
Let's discuss the meaning of an index
Let's discuss multivariate thinking
Let's discuss how statistics, data, modelling play a role in society and policy
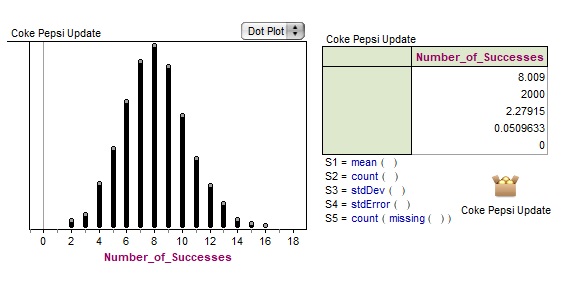
Experiments and Simulations - Coke vs Pepsi
This activity involves the following Ministry Expectations and can be used to connect these topics throughout the academic year:
A1.1, A1.3, A1.4, A2.2,
B1.1, B1.2, B1.3, B1.4, B1.7, B2.2, B2.6, B2.8,
C1.1, C1.2, C2.1, C2.4,
D1.2, D1.3, D1.4
Other Examples of Simulations include:
- Catch and Release Estimates
- Cholesterol Reduction Activity
- Chi-Squared Distributions
Applets
Brown University - Seeing Theory
This applet contains interactive visuals and an e-textbook that describes worked solutions.
I find this especially helpful for Venn diagrams and permutations/combinations.
Applets
Outstanding array of applets for every course topic. The visualizations are helpful for students to see simulations and sampling distributions and probabilities, and the apps include data.
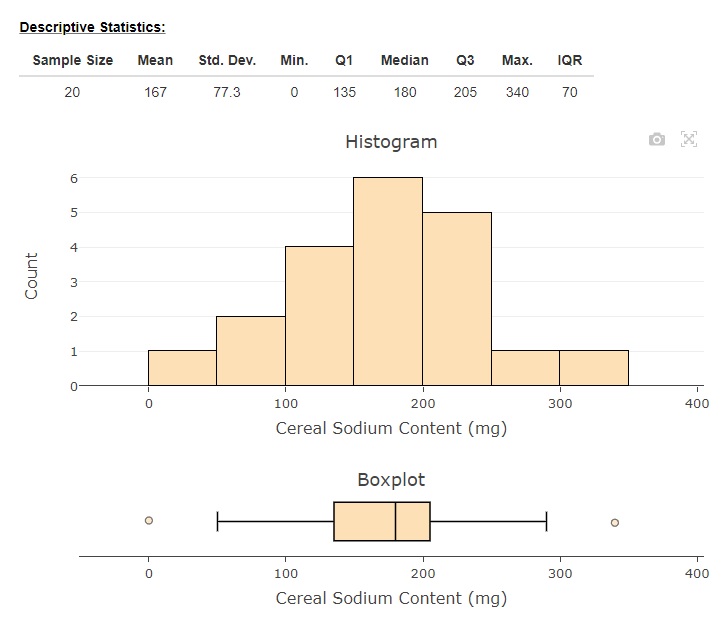
Applets
Outstanding array of applets for every course topic. The visualizations are helpful for students to see simulations and sampling distributions and probabilities, and the apps include data.

These applets are slick and offer a look at visualizing specific features of statistics and inference and distributions.
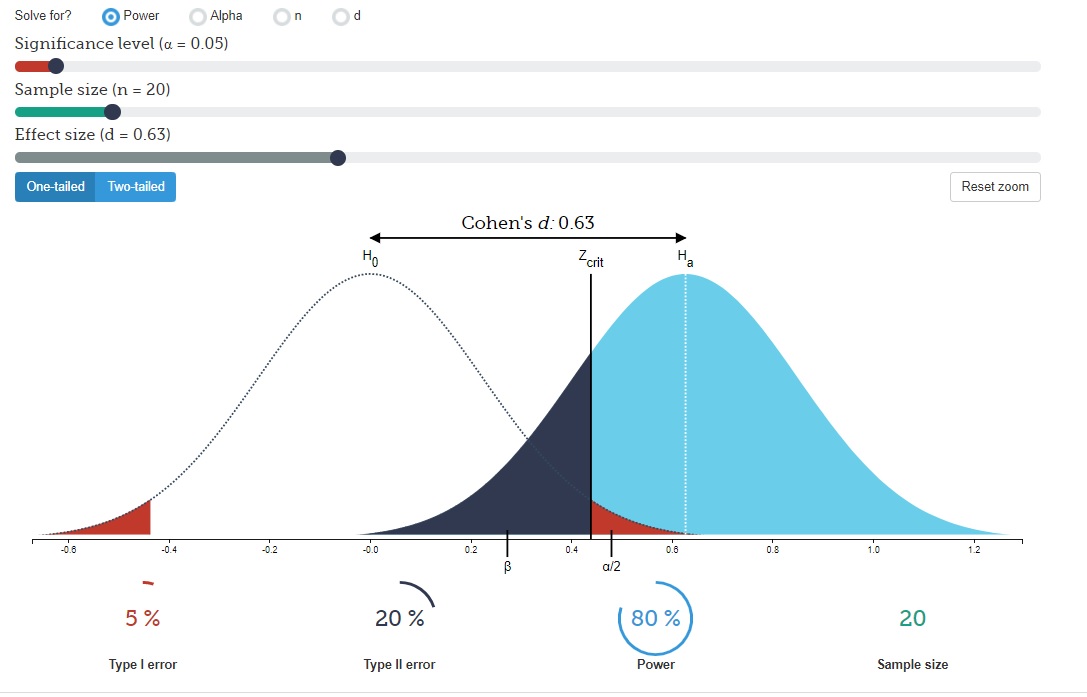
Ask Good Questions
Ask Good Questions
Allan Rossman, the inspiring former chief reader of the AP Statistics Program, encourages teachers to "ask good questions" for student learning. His blog is insightful, friendly, and encouraging to all. I have done several of his activities in my class.
Ask Good Questions
Allan Rossman, the inspiring former chief reader of the AP Statistics Program, encourages teachers to "ask good questions" for student learning. His blog is insightful, friendly, and encouraging to all. I have done several of his activities in my class.
This page offers all of the previous AP Free-Response Questions and Solution Rubrics.
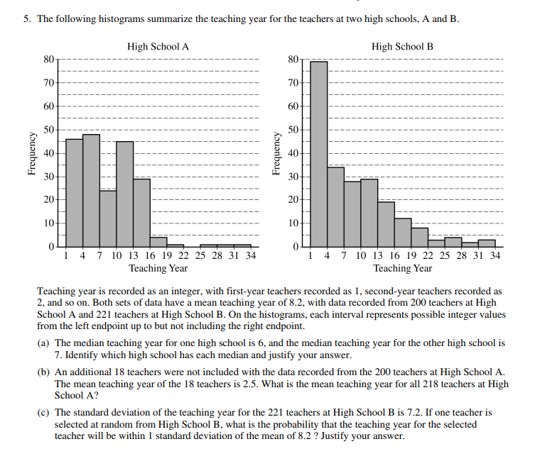
Assessment Strategies
Assessment Strategies
Formative Assessments (Unit)
- Submissions of Plots (COVID, StatsCan, Two-Way Tables)
- (Online) Discussion/Reflections on news articles or podcasts
- Quizzes (MC, Interpreting Plots)
- Group Presentations of Free Response Questions
- Collaborative Board Work
- Textbook Problems
Assessment Strategies
Formative Assessments (Unit)
- Submissions of Plots (COVID, StatsCan, Two-Way Tables)
- (Online) Discussion/Reflections on news articles or podcasts
- Quizzes (MC, Interpreting Plots)
- Group Presentations of Free Response Questions
- Collaborative Board Work
- Textbook Problems
Major Assessments - Find Data*
- Test/Exams (MC/Free-Response)
- Comparative Analysis with Software (1-Var)*
- Individual Analysis with Software (Z-scores)*
- Two Variable Modelling Investigation with Software (2-Var)*
- Simple Games and Simulations*
Extend Understanding Using the RStudio Learning Community
Use Data Science and RStudio to Develop Skills
I sometimes have students watch segments of David Robinson analyze TidyTuesday Data and explore some of it on their own.
I use the textbook OpenIntro Statistics for class and do several examples in my own RStudio during class to demonstrate Exploratory Data Analysis.
There are several resources offered through the RStudio Education Website using Rstudio cloud and the resources at R for the Rest of Us are helpful for further investigation.
Helpful Resources for Statistics Teachers
Anything from Dr. Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel although she focuses on introductory college-level instruction.
The Stats Medic and Skew the Script are free and offer lesson templates and plans to follow including discussion topics.
Amy Hogan's blog on teaching statistics has several tips from an experienced statistics teacher.
The AP Statistics YouTube Playlist offers video instruction of some key topics in the AP-Statistics Curriculum.
The New York Times Learning Network features What's Going On in This Graph? which features a graph and provides lesson and discussion forums for its interpretation.
The ASA produced a Guidelines for Assessment and Instruction in Statistics Education II: A Framework for Statistics and Data Science Education report (GAISE II).